Gout
Description
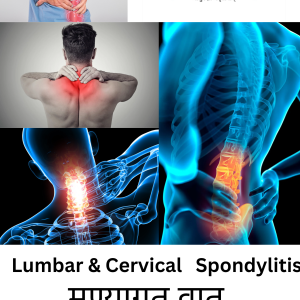
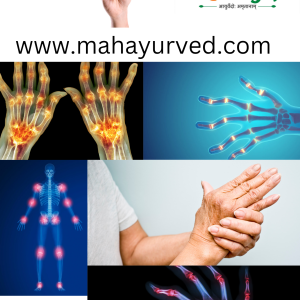
“Vatarakta” is an Ayurvedic term that translates to “gout” in English. It is a combination of two words: “Vata,” representing the Vata dosha, and “Rakta,” which means blood. Vatarakta is characterized by the accumulation of excessive Vata and impurities (ama) in the blood, leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling in the joints, particularly in the big toe, although other joints may also be affected.

According to Ayurveda, Vatarakta is primarily caused by dietary factors, lifestyle imbalances, and the accumulation of toxins (ama) in the body. Factors such as excessive intake of sour, spicy, and oily foods, alcohol consumption, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and genetic predisposition can contribute to the development of Vatarakta.
Ayurvedic treatment for Vatarakta aims to balance the doshas, eliminate toxins from the body, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms. Here are some common Ayurvedic approaches used for managing Vatarakta:
- Herbal Remedies:
- Ayurvedic herbs with anti-inflammatory, detoxifying, and diuretic properties are commonly used to reduce inflammation, remove toxins from the blood, and alleviate pain associated with Vatarakta. Examples include:
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
- Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa)
- Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia)
- Triphala (a combination of three fruits: Amalaki, Bibhitaki, and Haritaki)
- These herbs can be taken internally as decoctions, powders, or tablets.
- Ayurvedic herbs with anti-inflammatory, detoxifying, and diuretic properties are commonly used to reduce inflammation, remove toxins from the blood, and alleviate pain associated with Vatarakta. Examples include:
- Diet and Lifestyle Modifications:
- Following a diet that pacifies the aggravated doshas, particularly Vata and Pitta, can help reduce inflammation and support overall joint health. This may include consuming warm, nourishing, and easily digestible foods, as well as avoiding sour, spicy, and oily foods, alcohol, and red meat.
- Lifestyle recommendations may include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, practicing regular exercise, managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation and deep breathing exercises, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Ayurvedic Panchakarma:
- Panchakarma therapies, such as Basti (medicated enema), Virechana (therapeutic purgation), and Raktamokshana (bloodletting therapy), may be recommended to detoxify the body, balance the doshas, and alleviate symptoms of Vatarakta.
- External Therapies:
- Localized treatments such as Abhyanga (Ayurvedic oil massage) and Pinda Sweda (herbal poultice massage) can help reduce pain, inflammation, and stiffness in the affected joints.
- Specific Ayurvedic treatments like Patra Pinda Sweda (herbal bolus massage) or Choorna Pinda Sweda (dry herbal bolus massage) may be used to alleviate stiffness and improve mobility.
It’s important to consult with our a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner Dr Ravindra Borade at Maha Ayurved Clinic or online consultation for personalized treatment recommendations tailored to your individual constitution, symptoms, and medical history. Ayurvedic treatments for Vatarakta are often customized to address the underlying imbalances contributing to the condition and may involve a combination of therapies for optimal results. Additionally, it’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure that Ayurvedic treatments complement any conventional treatments you may be receiving for Vatarakta.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.