ALD – Alcoholic Liver Disease
Description
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a spectrum of liver conditions caused by excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption. It encompasses various stages, ranging from fatty liver (steatosis) to more severe conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Here’s an overview of alcoholic liver disease:
In Ayurveda, alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is understood as a condition primarily caused by an imbalance in the body’s doshas (bio-energies), particularly aggravated Pitta and Kapha doshas, as well as impaired digestion and metabolism due to prolonged alcohol consumption. Ayurvedic treatment for alcoholic liver disease focuses on restoring balance to the doshas, supporting liver function, detoxifying the body, and promoting overall health and well-being. Here are some Ayurvedic approaches that may be helpful in managing alcoholic liver disease: Dr. Ravindra Borade Founder of Maha ayurved having treated lot of patients having ALD
- Abstinence from Alcohol:
- The most important step in managing ALD from an Ayurvedic perspective is to stop drinking alcohol completely. This allows the body to begin the process of healing and detoxification.
- Dietary Recommendations:
- Following a Pitta and Kapha pacifying diet: Avoiding spicy, oily, fried, and processed foods, as well as excessive salt and sugar, which can aggravate Pitta and Kapha doshas and burden the liver.
- Favoring a diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean proteins.
- Including bitter and astringent tastes in the diet, such as bitter gourd, leafy greens, turmeric, and neem, to support liver health and detoxification.
- Drinking warm water with lemon juice in the morning to aid digestion and detoxification.
- Herbal Remedies:
- Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa): Known for its hepatoprotective properties, kutki is commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine to support liver function and regenerate liver cells damaged by alcohol.
- Bhumyamalaki (Phyllanthus niruri): Also known as “stonebreaker,” bhumyamalaki is used in Ayurveda to support liver health, promote bile secretion, and aid in the detoxification process.
- Triphala: A combination of three fruits (amalaki, bibhitaki, and haritaki) known for its detoxifying and rejuvenating properties. Triphala may help support liver function and improve digestion.
- Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa): Punarnava is believed to have diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce fluid retention and inflammation in the liver.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as yoga, walking, or gentle exercise, to improve circulation, metabolism, and overall well-being.
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques to support liver health and balance the mind-body connection.
- Getting an adequate amount of sleep each night to support the body’s natural healing processes.
- Detoxification Therapies:
- Panchakarma: Ayurvedic detoxification therapies such as Virechana (therapeutic purgation) and Basti (medicated enema) may be recommended under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner to remove toxins from the body, balance the doshas, and rejuvenate the liver.
-
- Fatty liver is the earliest stage of ALD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells due to excessive alcohol consumption.
- In this stage, the liver may become enlarged, but liver function is usually preserved.
- Fatty liver is reversible with abstinence from alcohol and lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis:
- Alcoholic hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the liver caused by long-term alcohol abuse.
- It is characterized by liver inflammation, liver cell damage, and sometimes liver failure.
- Symptoms may include jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and liver enlargement.
- Alcoholic hepatitis can be severe and life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Abstinence from alcohol is essential for the management of alcoholic hepatitis, along with supportive care and sometimes medications to reduce inflammation.
- Alcoholic Cirrhosis:
- Alcoholic cirrhosis is the most advanced stage of ALD, characterized by irreversible scarring (fibrosis) of the liver tissue.
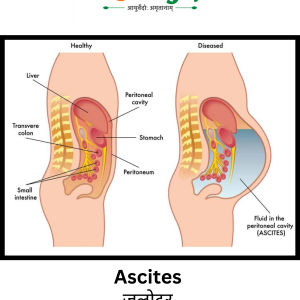
- In cirrhosis, healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, leading to impaired liver function and potential complications such as portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and liver failure.
- Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, jaundice, swelling in the abdomen and legs, easy bruising and bleeding, and confusion.
- Treatment for alcoholic cirrhosis focuses on managing complications, promoting liver function, and preventing further liver damage. Abstinence from alcohol is crucial to slow down or halt the progression of cirrhosis.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.